Unlocking the potential of operational efficiency

By BSc MSc staff reporter 03/09/2025
In today's fast-paced business landscape, operational efficiency is more crucial than ever. In this article, we'll explore the concept of operational efficiency, its benefits, and strategies for improvement.
What is Operational efficiency?
Operational efficiency is key to any successful organisation. It measures how a business uses resources such as time, money, and labour to produce goods or services. Operational efficiency refers to an organisation's ability to deliver high-quality products or services while minimising waste, reducing costs, and maximising productivity. Its practice involves streamlining processes, eliminating inefficiencies, and optimising resources for achieving better outcomes. A company is efficient when it can produce the same output with fewer resources or increase output with the same amount of resources.
Operational efficiency is key to streamlining processes, reducing waste, and maximising productivity. Management thinkers such as Fedrick Winslow Taylor emphasised the importance of efficiency in his book "The Principles of Scientific Management". The concept of operational efficiency is not new. Ford Motor Company's assembly line, which introduced the method in the early 20th century, is a classic example of operational efficiency in action. Toyota, a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer, uses operational efficiency through its Toyota Production System (TPS), a comprehensive lean management philosophy focused on eliminating waste and achieving continuous improvement.
Peter Drucker, a renowned management thinker and consultant, and credited as being the man who invented management, wrote extensively on the importance of efficiency and consulted with many companies, such as General Motors, General Electric, IBM, and Procter & Gamble, to improve and make more efficient their operations and management practices. Drucker's two-year analysis of General Motors resulted in significant financial organisational structuring, introducing ideas like employee ownership and shareholder value. He worked closely with Procter & Gamble to improve its operations. His consultancy expertise was employed by Intel, where his skills were used to influence management practices.
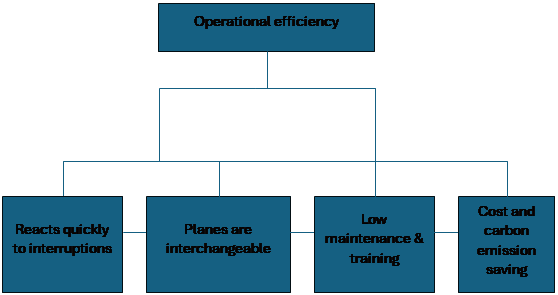
Toyota began transforming its operations, increasing efficiencies in the post WW11 area. They had developed the Toyota Production System in the 50's and 60's and allowed Toyota to become a leader in quality and efficiency by the 80's. Their manufacturing system was built on just-in-time inventory (JIT) and automated quality control, continuous improvement and waste elimination. Amazon achieved significant operational efficiencies by optimising its customer insight operations to improve logistics and shorten lead and delivery times. Southwest Airlines is a major American low-cost airline that specialises in short-haul flights. The company was founded in 1966 and provides a friendly, reliable, low-cost travel experience.
The Airline is a leader in the United States domestic market, carrying more passengers than any other airline. Southwest Airlines is efficient due to its low-cost business model, which works by minimising operational costs by using a single aircraft type, which enables it to reduce maintenance and training costs
Benefits of Operational Efficiency
1. Cost Savings: Operational efficiency helps reduce costs by minimising waste, reducing energy consumption, and optimising resources.
2. Increased Productivity: By streamlining processes and eliminating inefficiencies, operational efficiency can increase productivity and output.
3. Improved Quality: Operational efficiency can lead to improved quality products or services by reducing errors and defects. 4. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By delivering high-quality products or services quickly and efficiently, operational efficiency can enhance customer satisfaction.
5. Competitive Advantage: Organisations that achieve operational efficiency can gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Advantages of Operational Efficiency
1. Cost Savings: Operational efficiency helps reduce costs by minimising waste, reducing energy consumption, and optimising resources.
2. Increased Productivity: Streamlining processes and eliminating inefficiencies can increase productivity and output.
3. Improved Quality: Operational efficiency can lead to improved quality products or services by reducing errors and defects.
4. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Delivering high-quality products or services quickly and efficiently can enhance customer satisfaction.
5. Competitive Advantage: Organisations that achieve operational efficiency can gain a competitive advantage in the market. 6. Better Resource Allocation: Operational efficiency helps allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that resources are used where they are most needed.
Disadvantages of Operational Efficiency
1. Initial Investment: Implementing operational efficiency initiatives may require significant upfront investment in technology, training, or process redesign.
2. Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes to processes or procedures, which can make implementation challenging.
3. Over-Optimisation: Over-optimising processes can lead to rigidity and inflexibility, making it difficult to adapt to changing market conditions.
4. Potential for Job Losses: Operational efficiency initiatives may lead to job losses or restructuring, which can be challenging for affected employees.
5. Continuous Improvement Required: Operational efficiency is not a one-time achievement; it requires continuous monitoring and improvement to maintain efficiency gains.
6. Potential for Burnout: Overemphasising operational efficiency can lead to burnout among employees if they are expected to maintain high levels of productivity without adequate support or resources. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of operational efficiency, businesses can make informed decisions about how to implement and maintain efficient operations that benefit both the organisation and its employees.
The key components of operational efficiency : Strategies for Improving Operational Efficiency
1. Process Mapping: Identify and map out processes to understand where inefficiencies exist and opportunities for improvement.
2. Lean Principles: Apply lean principles to eliminate waste, reduce variability, and improve flow.
3. Automation: Automate repetitive or time-consuming tasks to free up resources and improve productivity.
4. Data Analysis: Use data analysis to identify areas for improvement and measure the effectiveness of operational efficiency initiatives.
5. Employee Engagement: Engage employees in the operational efficiency process to encourage ownership and drive cultural change.
6. Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are empowered to identify and solve problems.
Best Practices for Achieving Operational Efficiency
Before implementing any changes, it is best to conduct an efficiency audit and assess the organisation's current operations, including resources, technology and workflows. Identify bottlenecks and redundancies, and areas with high consumption to establish a performance baseline. Set clear, measurable goals for operational efficiency and track progress regularly. Streamline and optimise workflows, and unnecessary steps in workflow processes should be eliminated. Lean management, process mapping and Six Sigma should be deployed to decrease waste and increase productivity. Embrace technology and implement technology like AI and automation to handle repetitive, time-consuming tasks like data entry, invoicing and inventory management. Technology may also automate processes, improve productivity and improve operational efficiency. Monitor and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify areas for improvement. Empower employees to take ownership of processes and drive improvement initiatives. Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are encouraged to identify and solve problems.
Challenges in Achieving Operational Efficiency
Organisational and cultural, for example, employees may resist changes to processes or procedures, making it challenging to achieve operational efficiency. 2. Limited Resources: Limited resources, such as budget or personnel, can make it challenging to implement operational efficiency initiatives. 3. Complexity: Complex processes or systems can make it challenging to identify areas for improvement and implement operational efficiency initiatives.
Conclusion:
Operational efficiency is a critical component of any successful organisation. By understanding the benefits, strategies, and best practices for achieving operational efficiency, organisations can streamline processes, reduce waste, and maximise productivity. Whether you're a business leader, manager, or employee, operational efficiency can help you deliver high-quality products or services, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive business success.